18 Oct 2023
Australia’s Doherty Institute joins CEPI’s laboratory network to speed up development of epidemic and pandemic vaccines
The Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, a joint venture between The University of Melbourne and The Royal Melbourne Hospital, has joined CEPI’s Centralised Laboratory Network, the largest global group dedicated to the standardised testing of epidemic and pandemic vaccines. This is the latest laboratory to become a member of CEPI’s network – and the first in Australia – which will accelerate the development and evaluation of new vaccines for faster responses to a future epidemic or pandemic threat, thereby improving Australasia’s health security and minimising potential global disease burden.
Launched in 2020 in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, CEPI’s Centralised Laboratory Network is the largest global group providing and standardising testing support to vaccine developers free of charge* to epidemic and pandemic vaccine candidates undergoing preclinical and in-human testing. Compared to the typical process for evaluating vaccine candidates, where there is variability in trial data results as different tools and measurements are used at individual sites, laboratories within CEPI’s network use the same protocols and tools and materials, like assays and biological reagents**, to operate as though vaccines are all being tested ‘under one roof’, enabling uniformity in data readouts in the assessment of multiple different vaccine candidates.
Harmonised data can then inform researchers as to whether their candidate vaccines could advance into later stage clinical trials. It could also guide regulatory decisions and help to accelerate the development of new vaccines against CEPI’s priority pathogens (Lassa, Nipah, MERS, Ebola, Chikungunya, Rift Valley fever, COVID-19 and other Betacoronaviruses), other known threats (such as Marburg, Mpox), or a future Disease X – an unknown pathogen with epidemic or pandemic potential.
The work of the Centralised Laboratory Network is therefore a key enabler of the 100 Days Mission. Spearheaded by CEPI and embraced by the G7 and G20, the global goal aims to compress the time taken to develop vaccines against new threats to within 100 days of identification of a Disease X.
Expanding the network’s geographical footprint to include the Doherty Institute in Australia will help to reduce sample transfer and testing times for vaccine developers in the region, while also enhancing sustainable outbreak preparedness infrastructure globally.
Jane Halton, Chair of the CEPI Board, said: “Having CEPI’s Centralised Laboratory Network present and operational in Australia will be a major asset to vaccine developers across the region as they strive to defuse the threat of pathogens with pandemic potential in as little as 100 days. We are excited to welcome the Doherty Institute, with its world-class research expertise, as the first Australasian member of our growing global network.”
Professor Sharon Lewin, Director of the Doherty Institute, said: “COVID-19 showed us just how important global cooperation and collaboration is in producing vaccines at speed and scale. The Doherty Institute is delighted to become the first member in Australia to join CEPI’s global laboratory network initiative to ensure we are even better prepared to respond to the next pandemic.”
The Doherty Institute becomes the 16th member of CEPI’s Centralised Laboratory Network which now spans 14 countries.
Members apply to join the network through Calls for Proposals and are selected by CEPI experts based on their successful track record in testing clinical samples under high-quality systems and their willingness to handle high volumes from multiple regions.
Over the course of its three years of running, the network has provided preclinical to Phase III clinical trial support to more than 50 vaccine developers and tested approximately 100,000 samples. The network has also supported identification of correlates of protection for vaccines, and assisted in capacity-building programmes and technology-transfer programmes.
CEPI has, to date, provided up to US $25 million to support the running of the network.
As part of its pandemic preparedness plan, CEPI is increasing the number and global diversity of laboratories within the Centralised Laboratory Network to ensure strategic coverage on every continent for faster response to emerging infectious disease outbreaks.
Notes:
*CEPI-funded and non-CEPI-funded vaccine developers are eligible to use the network for vaccine testing to ensure all can benefit from this analysis. Samples shipment cost and documentation related to the shipment is the vaccine developer’s responsibility.
** Standardised assays test for the presence of specific antibodies—indicative of an immune response—following either natural infection or vaccination and biological reagents are used for the detection or determination of substances. In addition to testing vaccine samples, The Doherty Institute will develop assays to be used by the network.
CEPI’s Centralised Laboratory Network
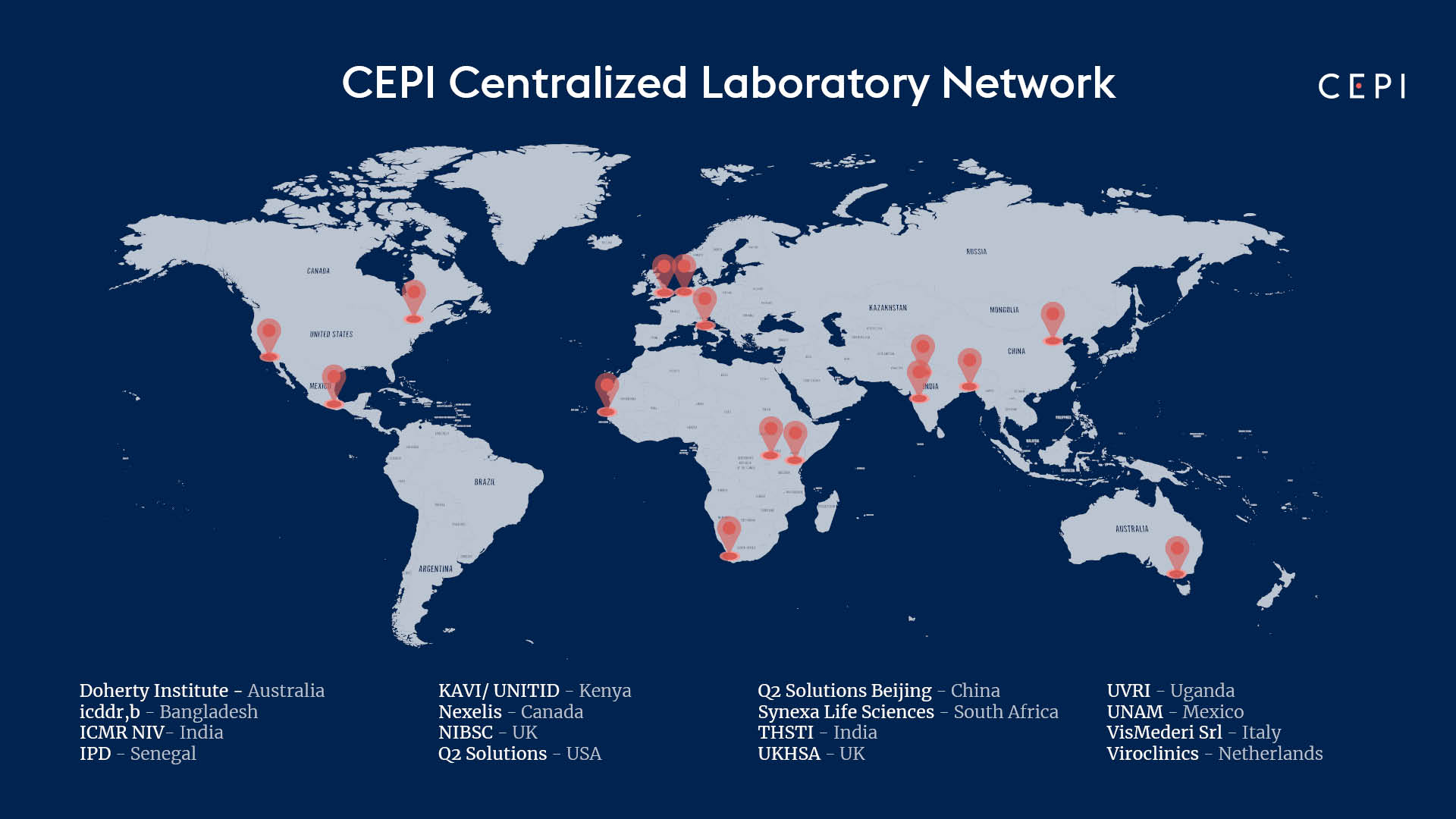
CEPI’s Centralised Laboratory Network includes the following members:
- Doherty Institute (Australia)
- International Centre for Diarrheal Disease Research (icddr,b) (Bangladesh)
- National Institute for Biological Standards and Control (UK)
- Nexelis (Canada)
- Q2 Solutions (China)
- Q2 Solutions (USA)
- Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (India)
- UK Health Security Agency (UK)
- Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (Mexico)
- Viroclinics (Netherlands)
- Vismederi (Italy)
- Indian Council of Medical Research National Institute of Virology (ICMR NIV) (India)
- Institut Pasteur de Dakar (IPD) (Senegal)
- KAVI Institute of Clinical Research (KAVI ICR) & University of Nairobi Institute of Tropical and Infectious Diseases (UNITID) (Kenya)
- Synexa Life Sciences (South Africa)
- Uganda Virus Research Institute (UVRI) (Uganda)
Each member will be on standby to support the rapid development of novel vaccines against a future Disease X by developing assays, supporting technology transfer of these assays to other laboratories, and testing samples from clinical trials of potential vaccine candidates against such pathogens. In interepidemic periods, the facilities will provide the same services to support vaccine development against one or more of CEPI’s priority diseases identified on the World Health Organization R&D Blueprint as having epidemic potential or as a major public health risk. CEPI promotes knowledge and collaboration by members of the network to increase access to capabilities, technologies, and infrastructure and enhance pandemic preparedness efforts.
CEPI-funded vaccine developers are encouraged but are not obliged to use the Centralised Laboratory Network. Results produced will be sent back to the vaccine developer – neither CEPI nor the laboratory who assessed the preclinical or clinical samples will own the data.
Further information on the Centralised Laboratory Network is available in ‘The CEPI centralized laboratory network for COVID-19 will help prepare for future outbreaks’, article published in Nature in September 2023.
This media release was distributed by CEPI and the Doherty Institute in Australia and globally on Wednesday 18 October, 10am (AEDT). Click here to download the media release (PDF).


